The UAVF ROS Package
The uavfpy package in main is a python package that does not depend on ROS. We do use ROS to orchestrate the mission, so we have a ROS package as well.
uavfros is the name of the ROS package. Its development shares an issue tracker and repository with the main python package, but its development happens on the ROS and ROS-dev branches of the repository.
Installation
Prerequisites
In order to develop packages on ROS, you need a PC equipped with Linux. Any desktop linux platform is suitable, but the easiest by far is Ubuntu. I prefer Ubuntu MATE on the desktop, but you can use a standard Ubuntu, KDE, or whichever flavor you like.
uavfros is a ROS package. To install it, you need to have ROS installed and configured. That will not be covered in this documentation; if you are brand new to ROS, I recommend that you go through the ROS tutorial 1 before continuing to the next section.
Note
In order to run Gazebo simulations, you need to have installed the “full” ROS environment. For example, with apt, you have installed ros-noetic-desktop-full, not ros-noetic-ros-base or ros-noetic-desktop.
This release targets ROS 1 Noetic, for compatibility reasons. We are not developing for ROS 2.
We assume that you have set up a catkin workspace in your home directory:
~/catkin_ws
(Simulation) Install and Run PX4
Follow this guide if you are planning to simulate a PX4 UAV mission.
This guide based on the PX4 ROS1 Interface Guide.
First, clone the PX4-SITL_gazebo repository into any directory. Make sure that you clone recursively and that you do not clone into your catkin_ws:
cd ~/
git clone --recursive https://github.com/PX4/PX4-Autopilot.git
Build the autopilot and make the SITL simulation available to ROS:
cd ~/PX4-Autopilot
DONT_RUN=1 make px4_sitl_default gazebo
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
source Tools/setup_gazebo.bash $(pwd) $(pwd)/build/px4_sitl_default
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:$(pwd)
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:$(pwd)/Tools/sitl_gazebo
You will then see that px4 is available to your roslaunch. Run:
roslaunch px4 mavros_posix_sitl.launch
A gazebo window showing a quadcopter will open and the simulation will start. You will see a bunch of messages appear in the console window. Make sure you keep the console window open.
Inspect the rqt_graph:
rqt_graph
You will see several new nodes:
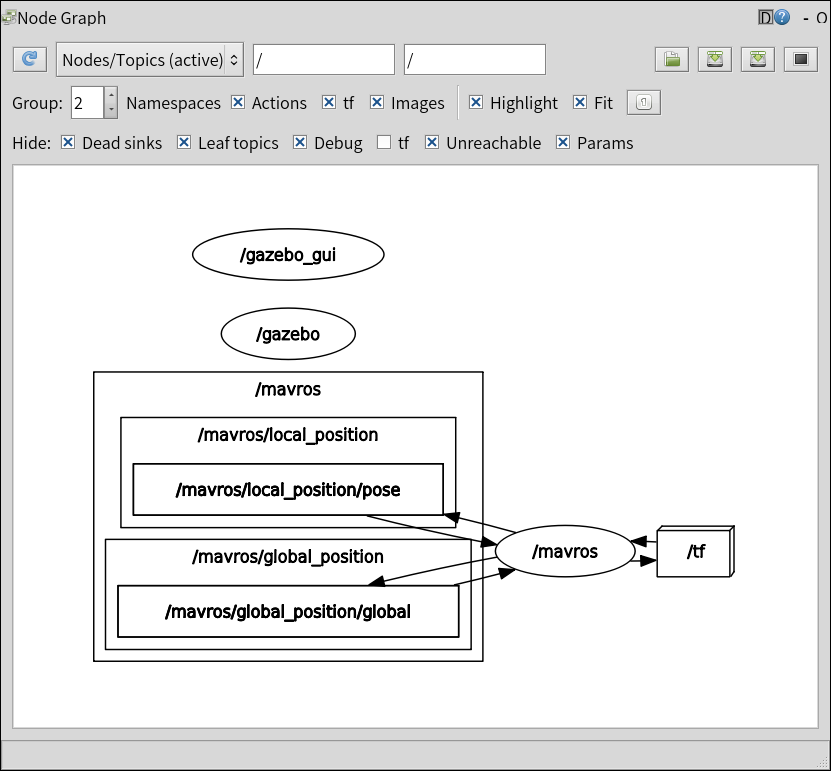
This is the simulated PX4, which can be commanded with MAVROS.
Install uavf
Warning
Because we are using this package from ROS, we need to ensure that we are NOT in any python virtual environment. You can verify this by typing which python into a terminal window. Make sure that the output is /usr/bin/python.
Set up ROS:
source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash
Clone the git repository into ~/catkin_ws/src and checkout the ROS branch. If you are developing ROS functionality, checkout ROS-dev.
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/uci-uav-forge/uavf
git checkout ROS
Install the auvsi_suas interop client package and the uavf python package to your system python. There is a script that will do this.
cd ~/catkin_ws/src/uavf/
bash ./install_deps.sh
Note
If, for some reason, you need to uninstall auvsi_suas from your system python, you can do so by running pip uninstall auvsi_suas.
Run catkin_make and source your devel/setup.bash file:
cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin_make
source devel/setup.bash
Make sure you remember to start a roscore instance in a separate terminal window.
Running a Mission with uavfros
Until we have viable hardware testing, this section deals with running a simulated mission with uavfros.
Run uavfros Interop
The interop client is a ros node written in Python. We start it with rosrun.
rosrun uavfros interop
Run uavfros Planner
The navigation node is a ros service node that will generate a new path for the UAV to follow between waypoints.
rosrun uavfros planner
Run uavfros GNC
The uavf GNC node is a ros node that will take a computed plan and manage the execution of the plan on the UAV.
rosrun uavfros gnc